| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- 옵티마이저
- pytorch
- 알고리즘
- ViT
- 파이토치
- transformer
- Self-supervised
- 프로그래머스
- optimizer
- 딥러닝
- 코드구현
- 논문 리뷰
- cnn
- Convolution
- 인공지능
- 코딩테스트
- 머신러닝
- 논문리뷰
- 파이썬
- programmers
- 논문
- object detection
- Computer Vision
- Semantic Segmentation
- Python
- Ai
- Segmentation
- opencv
- 논문구현
- Paper Review
Archives
- Today
- Total
Attention please
데이터 시각화(tick label & tick param & text) - matplotlib 본문
데이터 시각화/matplotlib
데이터 시각화(tick label & tick param & text) - matplotlib
Seongmin.C 2022. 11. 18. 11:38728x90
tick label
matplotlib 패키지의 boxplot 함수를 사용하여
상자그림을 그릴 수 있습니다.
이번에는 이 상자그림을 그린 후 각각의 상자에 대해 tick을 부여한 후
각 tick에 이름을 부여하도록 하겠습니다.
fig = plt.figure(figsize = (10,5), dpi = 100)
ax = fig.subplots()
data1 = np.random.normal(0,1, size = (1000,5))
_=ax.boxplot(data1)
_=ax.set_xticks([1,2,3,4,5])
_=ax.set_xticklabels(['월', '화', '수', '목', '금'], fontsize=13)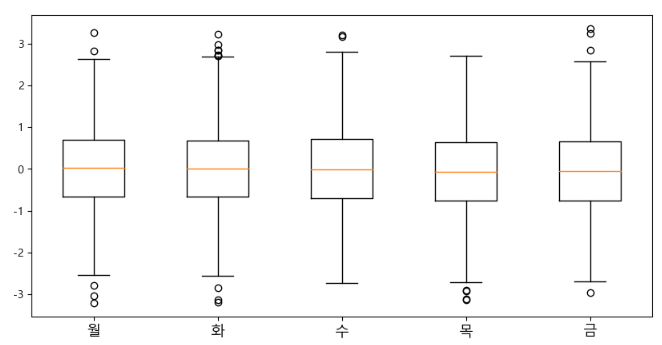
이와 같이 각 상자그림이 무엇을 그리고자 하였는지
set_xticklabels 함수를 사용하여 그릴 수 있습니다.
Tick params
tick_params 함수를 사용하여
Axes에 삽입한 tick의 각종 style을 수정하는 것이 가능합니다.
이중 axis 파라미터는 어떤 축의 tick을 수정할 것인지 결정할 수 있으며
length 파라미터를 설정하여 tick의 길이를 설정할 수 있습니다.
이때 length 파라미터를 이용하여
불필요한 tick을 제거하는 것이 가능합니다.
fig = plt.figure(figsize = (12, 4), dpi = 100)
axs = fig.subplots(1,2)
d1 = np.random.normal(0, 2, 1000)
d2 = np.random.normal(1, 2, 1000)
d3 = np.random.normal(4, 2, 1000)
d4 = np.random.normal(3, 2, 1000)
_=axs[0].boxplot([d1,d2,d3,d4], positions=[1,1.5,3,3.5])
_=axs[0].set_xticks([1.25, 3.25])
_=axs[0].set_xticklabels(['남자', '여자'], fontsize=16)
_=axs[1].boxplot([d1,d2,d3,d4], positions=[1,1.5,3,3.5])
_=axs[1].set_xticks([1.25, 3.25])
_=axs[1].set_xticklabels(['남자', '여자'], fontsize=16)
_=axs[1].tick_params(axis='x', length=0)

이번에는 tick_param 함수의 다른 파라미터를 입력하여
스타일을 지정시켜보겠습니다.
fig = plt.figure(figsize = (10,5), dpi = 100)
axs = fig.subplots(1,2)
m1 = 3
s1 = 5
data = np.random.normal(m1, s1, size = 10000)
_=axs[0].hist(data, bins = 30, edgecolor = 'k')
_=axs[0].set_xticks([m1])
_=axs[0].set_xticklabels([f'$\\mu$={m1}'], fontsize=16)
_=axs[0].set_xlabel('xlabel', fontsize=20)
_=axs[1].hist(data, bins = 30, edgecolor = 'k')
_=axs[1].set_xticks([m1])
_=axs[1].set_xticklabels([f'$\\mu$={m1}'], fontsize = 16)
_=axs[1].set_xlabel('xlabel', fontsize = 20)
## tick 스타일 설정
_=axs[0].tick_params(axis='both', direction='inout', width = 5,
length=10, color = 'c')
_=axs[1].tick_params(axis='x', direction='out', width = 5,
length=10, pad=20, color = 'y',
labelcolor = 'g', labelsize=30)
_=axs[1].tick_params(axis='y', direction='inout', width=2,
length=20, pad=10, color='r',
labelcolor='b', labelsize=15)
Text
text함수를 사용하여 text box를 생성하여
그림을 그리는 것이 가능합니다.
fig = plt.figure(figsize = (5,5), dpi = 100)
ax = fig.subplots()
def aa(X):
return 0.25 * (X+4) * (X+1) * (X-2)
X = np.linspace(-5, 3, 1000)
Y = aa(X)
_=ax.plot(X,Y)
_=ax.set_title('$f(x)=\\frac{1}{4}(x+4)x(x+1)(x-2)$')
# 최대와 최소점의 x 좌표
max_x = -2.75
min_x = 0.75
# 최대와 최소점의 y 좌표
max_y = aa(max_x)
min_y = aa(min_x)
# text box 그리기
ax.text(max_x, max_y, 'local maximum', fontsize=15,
ha = 'center', va = 'bottom')
ax.text(min_x, min_y, 'minimum', fontsize=15,
ha = 'center', va = 'top')
# 해당 text box 의 좌표에 점 찍기
ax.scatter([max_x, min_x],[max_y, min_y], c = 'r')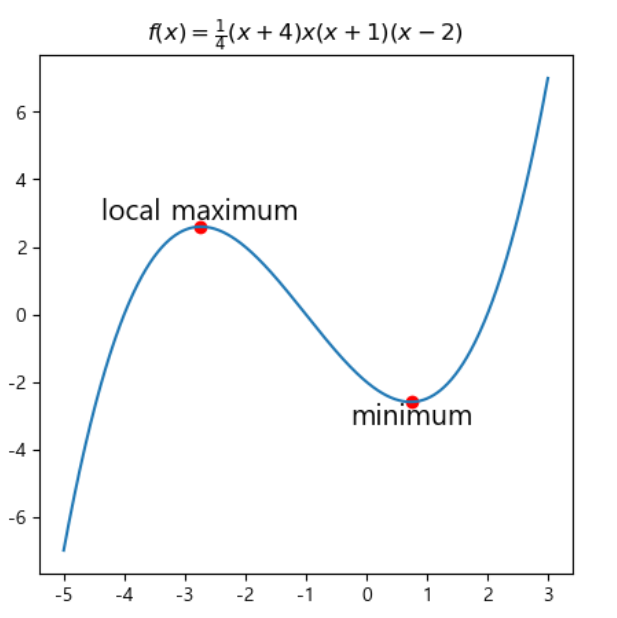
또한 text 함수의 bbox 파라미터를 사용하여
해당 text box의 스타일을 딕셔너리에 미리 저장한 후
적용하는 것이 가능합니다.
box1 = {'facecolor':'b',
'edgecolor':'k',
'alpha':0.5,
'boxstyle':'square',
'pad':0.5}
box2 = {'facecolor':'lightblue',
'edgecolor':'steelblue',
'alpha':0.9,
'boxstyle':'round',
'pad':0.2}
ax.text(max_x, max_y, 'local maximum', fontsize=15,
ha = 'center', va = 'bottom', bbox=box1)
ax.text(min_x, min_y, 'minimum', fontsize=15,
ha = 'center', va = 'top', bbox=box2)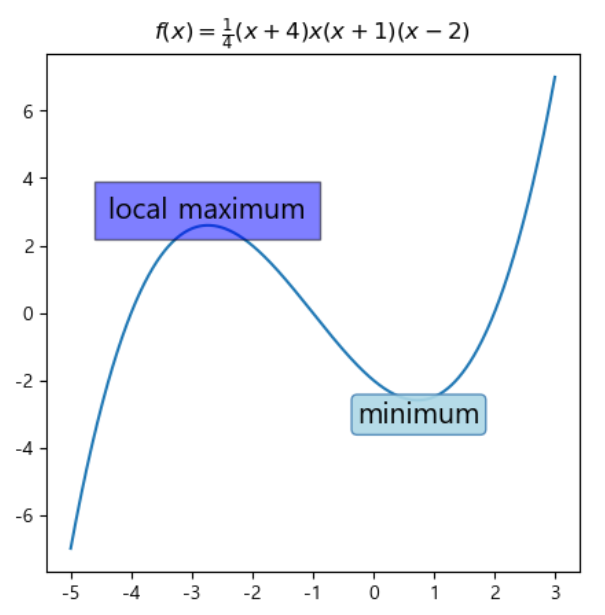
728x90
'데이터 시각화 > matplotlib' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 데이터 시각화(legend) - matplotlib (0) | 2022.11.21 |
|---|---|
| 데이터 시각화(title & lim & tick) - matplotlib (0) | 2022.11.17 |
| 데이터 분석;boxplot으로 중요한 피처 구분하기 - matplotlib (0) | 2022.10.12 |
| Color와 Style 사용하기 - matplotlib (0) | 2022.10.08 |
| 상자그림 그리기(boxplot) - matplotlib (0) | 2022.10.08 |
Comments




